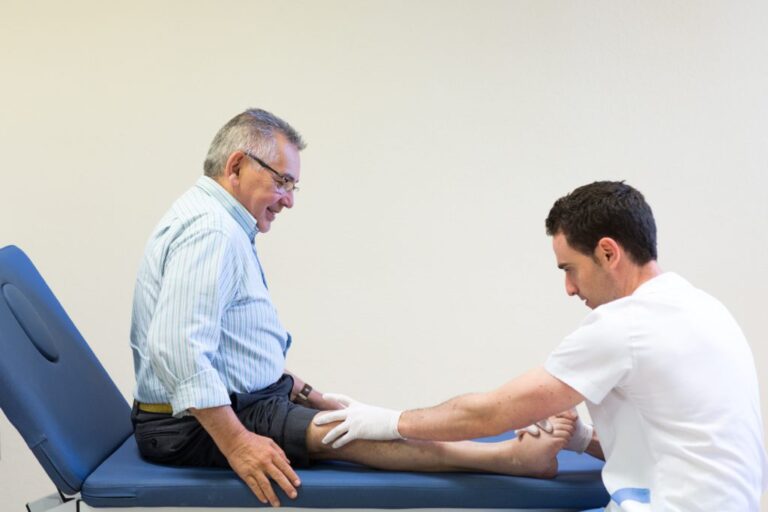
A broken femur in older people is a serious injury that can have important physical and emotional consequences. Let us remember that the femur is the longest and strongest bone in the body, but we should not understand this health problem as a simple fracture of a long bone, but as a serious condition that affects the physiological and functional situation of the person and causes their underlying diseases to decompensate.
This happens because the majority of femur breaks in the elderly occur in the femoral neck or in other areas close to the hip joint, which has important consequences in terms of mobility, independence and quality of life. In fact, The fatality rates due to a broken femur in the elderly are very high, ranging between 26 and 33% one year after suffering the fracture. And less than half of older people who suffer this injury are able to walk again as before.
Types of femur fractures in older people
There are different types of femur fractures. Taking into account its location, the femur fracture can be:
- Intracapsular fracture
They are fractures that occur at the level of the neck and head of the femur, and are generally within the capsule, which is the soft tissue envelope that contains the lubricating and nutritional fluid of the hip joint. This type of fracture can lead to loss of blood supply to the bone, with a consequent high risk of necrosis.
- Intertrochanteric fracture
We call this the fracture that occurs between the neck of the femur and the greater trochanter and the lesser trochanter. The lesser and greater trochanter are two bony prominences that act as a point of attachment to important muscles of the hip. They are extracapsular fractures, so they rarely compromise the irrigation of the head of the femur, therefore, the risk of necrosis is minimal.
- Subtrochanteric fracture
This fracture occurs below the lesser trochanter, specifically in a region between the lesser trochanter and an area approximately 5-6 cm below, that is, below the trochanters and close to the rest of the bone.
- Femoral shaft fracture
It is one that occurs along the rest of the femur and can be of different types, such as spiral, oblique or transverse fractures.
Recovery of a broken femur in older people
Recovery from a broken femur in older people can be a long process, even taking 6 months to completely heal. However, the length and success of recovery depends on several factors, including the severity of the fracture, the health of the patient, the presence of pre-existing medical conditions, and the speed with which treatment and rehabilitation is initiated.
When a femur break occurs in older people, the first consequence is intense pain. In addition to medication, it will be necessary to immobilize the person and possibly require the placement of an orthopedic device to stabilize the fracture.
In most cases of broken femur in the elderly, it is necessary to undergo the operating room to align and fix the bone.
After surgery and hospital discharge, the process does not end, but rather physiotherapy treatment begins so that the person can regain strength and mobility. Also, in some cases, occupational therapy may be necessary to help the person adapt to the temporary or permanent limitations that have been generated.
This rehabilitation process is usually prolonged and can be carried out at home or in social and health centers. But taking into account that a month after surgery, the majority of older people still cannot move around alone, many prefer to move to a residential center to replace their home so that they can have the necessary help and care until they regain autonomy.
It must also be taken into account that, during recovery, the person’s abilities to carry out daily activities independently will be affected, which, in turn, represents an emotional impact that is added to the physical situation.
How to help an elderly person with a broken femur
To help an elderly person who has suffered a broken femur, it is necessary to dedicate a lot of time to attention and care with large doses of patience. It must be taken into account that it will be necessary to make changes and adjustments to adapt to the new circumstances:
Coordinate medical care
Make sure the person receives immediate medical attention and follows the treatment plan recommended by health professionals. You will have to be attentive to administering prescribed medications, assisting in physical therapy sessions, and accompanying the elderly person to medical appointments to ensure that they understand the instructions and the treatment plan.
Importance of generating a safe environment
You will need to make modifications to the home to ensure a safe environment, such as installing handrails, grab bars, a new bed, relocating furniture to make everything more accessible, and removing obstacles to create clearer spaces.
Safe Mobilization
You will have to help the person move, respecting medical restrictions and recommendations. To do this, you may use assistive devices such as crutches, walkers, or wheelchairs as necessary.
Help in daily activities
After a broken femur in older people, it is very necessary to provide assistance in daily activities, such as dressing, bathing, cooking,… The environment will have to be adapted as much as possible to facilitate these activities.
Stimulate mental activity
Do not forget to provide activities to keep the mind active and prevent cognitive deterioration during the recovery period, such as reading, board games, puzzles, calculation, writing, crosswords, sudoku or others following specific applications (as an example).
Tries to promote their independence
In the same way that we provide care and attention to the elderly person, we must also encourage them to be as independent as possible, within the limitations of their injury, and to perform certain light tasks on their own.
Emotional Support
Understand that a femur fracture can be a painful and discouraging experience. Offer emotional support and listen to their concerns. Anxiety and fear can be part of recovery.
The role of the caregiver is essential to achieve optimal recovery, but remember that you can involve other family members, or friends, to distribute responsibilities. Or, you can go to a specialized rehabilitation center attended by different highly trained health professionals: rehabilitation doctors, physiotherapists, occupational therapists and nutritionists. In addition to being a safe and stimulating environment for patients, NAMI’s specialized centers guarantee comprehensive and continuous care until the person regains their autonomy.