Aging naturally entails a series of changes in our body. One of the most common, but often overlooked, problems are blood circulation problems.
These problems can manifest themselves in various ways and, although they are common in the elderly, there are strategies to prevent them or at least reduce their impact. Therefore, below, we will offer you a complete guide on how to detect and prevent these problems.
Symptoms of circulation problems
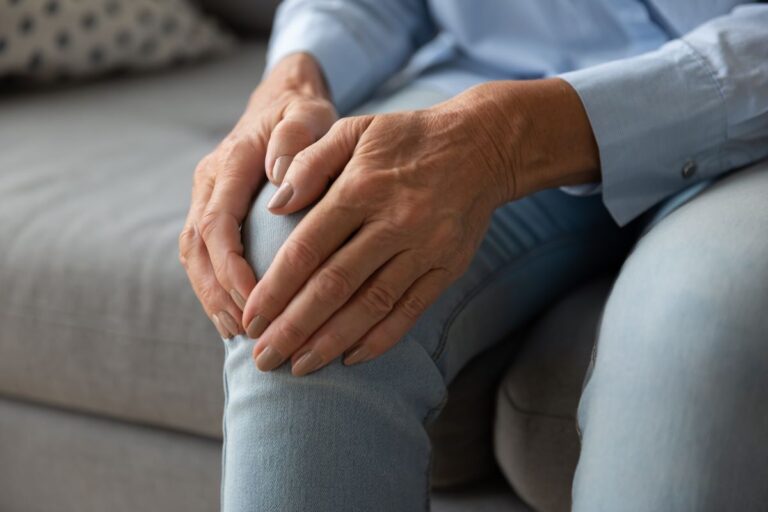
The symptoms of circulation problems are varied and can vary in severity from one person to another. Some of the most common include:
- Cold legs and feet or numb.
- Color changes in the skin, such as paleness or bluish discoloration.
- Swelling in feet, ankles and hands.
- Varicose veins or spider veins.
- Ulcers on the feet and ankles that do not heal quickly.
Causes of circulation problems in older people
The causes of poor circulation are diverse, some directly related to aging and others to lifestyles or medical conditions. The main causes include:
-
Aging: As we age, the walls of our arteries can become stiffer and less flexible. This can hinder blood flow and increase blood pressure, leading to circulatory problems.
-
Accumulation of plaques: Over time, fat deposits, cholesterol and other substances may accumulate on the walls of the arteries, forming plaques. These plaques can narrow the arteries and reduce blood flow, known as atherosclerosis.
-
Hypertension: High blood pressure is common in older people and can damage the walls of the arteries, weakening them and affecting circulation.
-
Diabetes: older people with diabetes can develop damage to their blood vessels, which can make circulation difficult and increase the risk of heart problems.
-
Lifestyle: Factors such as lack of physical activity, an unhealthy diet, smoking and excess weight can contribute to circulatory problems in older people.
-
Heart diseases: Heart conditions, such as heart failure or arrhythmias, can weaken the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently, affecting circulation.
-
Blood clots: Older people are at higher risk of developing blood clots, which can block blood flow and cause circulatory problems.
-
Lack of activity: Physical inactivity can weaken muscles and reduce the efficiency of the overall circulatory system.
-
Peripheral vascular disease: This condition is characterized by a narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the extremities, which can cause pain and difficulty moving.
-
Genetics: Family history can influence a person’s predisposition to circulatory problems.
-
Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to hypertension and damage the circulatory system.
- Lack of hydration: Dehydration can make the blood thicker, making it difficult for it to circulate through the arteries.
It is important to remember that each person is unique and may face circulatory problems for different reasons. Therefore, consulting with a health professional can help identify the specific causes and establish an appropriate management plan to maintain healthy circulation in old age.
How do I know if I have circulation problems?
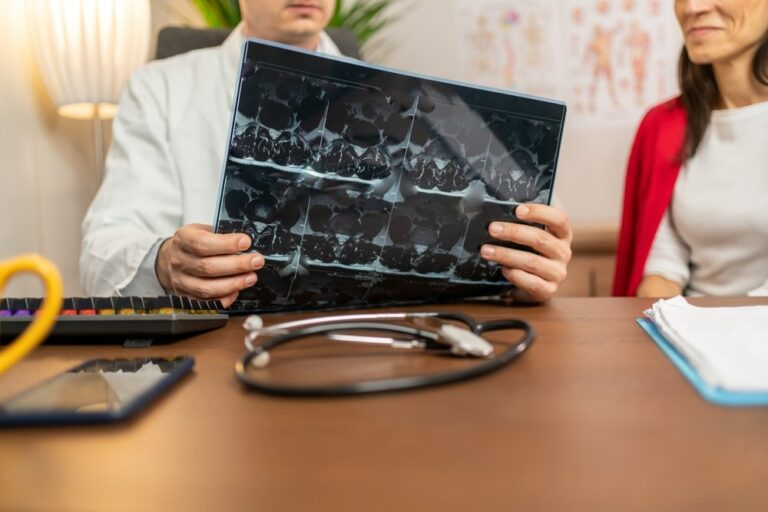
To determine how to know if I have circulation problems, it is best to pay attention to the symptoms mentioned above and go to a doctor if you detect any anomaly.
A doctor may perform specific tests, such as imaging studies or blood pressure tests on different parts of the body, to diagnose blood circulation problems.
How to prevent poor circulation in older people?
Prevention is always the best strategy. Here are some tips to prevent circulation problems:
Perform exercise
Regular exercise is essential to maintain good circulatory health. You don’t need to run marathons; Walking, swimming or doing low-impact exercises for 30 minutes a day can make a big difference.
Take care of your food
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains can help improve circulation. Limiting your intake of saturated fats, salt and added sugars is crucial.
In addition, consuming foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3s can help prevent hardening of the arteries.
Put your feet up
Especially if symptoms of circulation problems have already been detected, it is useful to elevate the legs above the level of the heart several times a day. This helps blood return to the heart and can reduce swelling and other symptoms.
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption
Tobacco is an enemy of circulation, since it narrows and hardens the arteries. Alcohol, on the other hand, should be consumed in moderation. Excessive consumption can raise blood pressure and negatively affect circulation.
Wear appropriate clothing
Avoid clothing or shoes that are too tight. Excessive compression can hinder circulation, especially in the ankles and legs.
As you see, although circulation problems are common in older people, it is not inevitable to suffer from them. With a healthy lifestyle and paying attention to our body’s signals, we can prevent or manage these problems to have a more active and healthy old age.